
How to Use GROUP BY and ORDER BY clauses

By Chinaza MaryTheresa Akwue
In the previous article, we discussed two major SQL clauses: the WHERE and LIMIT clauses. To read the article if you haven't already, visit this LINK.
In this article, we'll explore how these two Group BY and ORDER BY clauses work.
Understand the GROUP BY Clause
The GROUP BY clause is used to group rows based on specific columns. It's often used with aggregate functions like COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, and MAX to calculate summary statistics for each group.
Basic Syntax
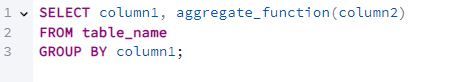
Breakdown:
- SELECT column1, aggregate_function(column2): This part selects the columns you want to display. column1 is the column you want to group by, and aggregate_function(column2) applies an aggregate function (like SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, or MAX) to the specified column.
- FROM table_name: Specifies the table from which you'll retrieve data.
- GROUP BY column1: Groups the result set by the specified column.
Example:
Suppose you have a table named payment with columns customer_id and amount. To calculate the total amount for each customer_id, you would use the following query:
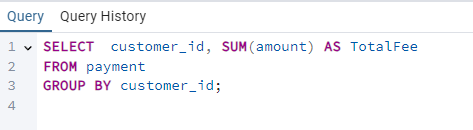
This query will group the rows by customer_id and calculate the sum of the amounts for each group.
Result:
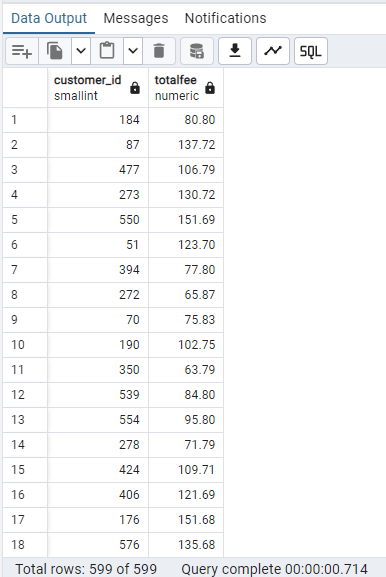
Understand the ORDER BY Clause
The ORDER BY clause is used to sort the result set based on one or more columns. You can specify ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order.
Basic syntax
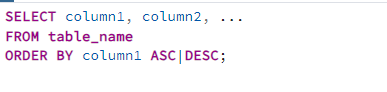
Breakdown:
- SELECT column1, column2: Specifies the columns you want to retrieve.
- FROM table_name: Specifies the table from which you'll retrieve data.
- ORDER BY column1 ASC|DESC; Sorts the result set based on the specified columns.
- ASC: Ascending order (default)
- DESC: Descending order
Example:
Suppose you have a table named payment with columns customer_id and amount. To arrange your results in descending order, you would use the following query:
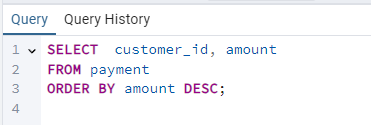
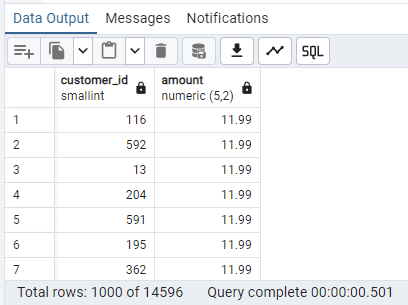
This query will sort the results by amount in descending order.
Result:
Combining GROUP BY and ORDER BY
You can combine both clauses to group data and then sort the results. For instance, to group payment by customer_id and then sort the results by total amount in descending order:
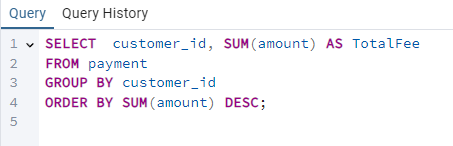
Result:
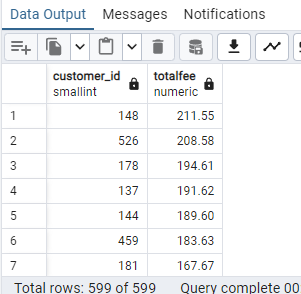
Conclusion
By effectively utilizing the GROUP BY and ORDER BY clauses, you can extract valuable insights from your data and present it in a clear and organized manner. The GROUP BY clause allows you to categorize data based on specific criteria, while the ORDER BY clause enables you to sort the results in a desired sequence. By combining these two clauses, you can gain a deeper understanding of your data and make informed decisions.
To further enhance your SQL skills, join our next data bootcamp!
- Understand the GROUP BY Clause
- Understand the ORDER BY Clause
- Combining GROUP BY and ORDER BY
- Conclusion
Empowering individuals and businesses with the tools to harness data, drive innovation, and achieve excellence in a digital world.
2026Resagratia (a brand of Resa Data Solutions Ltd). All Rights Reserved.
