
Report Automation in Power Query

Admin
Instructor: Pushkar Bhamare (LinkedIn)
Power Query is a data connection and transformation tool that is built into Microsoft Excel and other Microsoft products such as Power BI and Microsoft Access. It allows you to import, transform, and clean data from a variety of sources, including files, databases, web pages, and other data sources.
With Power Query, you can easily reshape and combine data, apply filters and calculations, merge data from different sources, and create custom data transformations. It is particularly useful when dealing with large and complex data sets, as it enables you to automate the data cleaning and transformation process, saving time and effort.
Power Query also includes a user-friendly interface that allows you to preview and edit the data transformations in real-time, making it easy to see how your data will look after the transformations have been applied.
In this data digest episode, I will walk you through the following highlighted below:
- Data source options in Power Query
- Load data from folder in Power Query
- Close and load option and data types
- Split and extract operation in Power Query
- Merge queries in Power Query
- Conditional column in Power Query
- Group by function in Power Query
- Unpivot and pivot columns in Power Query
- Append queries in Power Query
Let’s get started…
Data source options in power query
Power Query provides various data source options that you can use to connect to and import data from different types of data sources. Some of the common data source options available in Power Query include:
- File-based sources: You can import data from files such as Excel workbooks, CSV files, text files, XML files, JSON files, and folders.
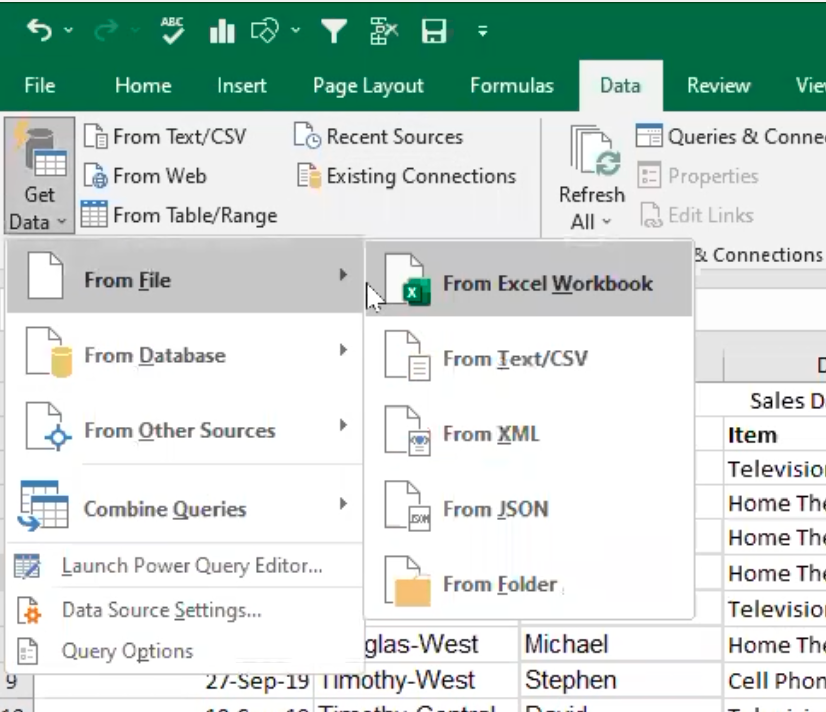
- Database sources: You can connect to and import data from different types of databases such as SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and others.
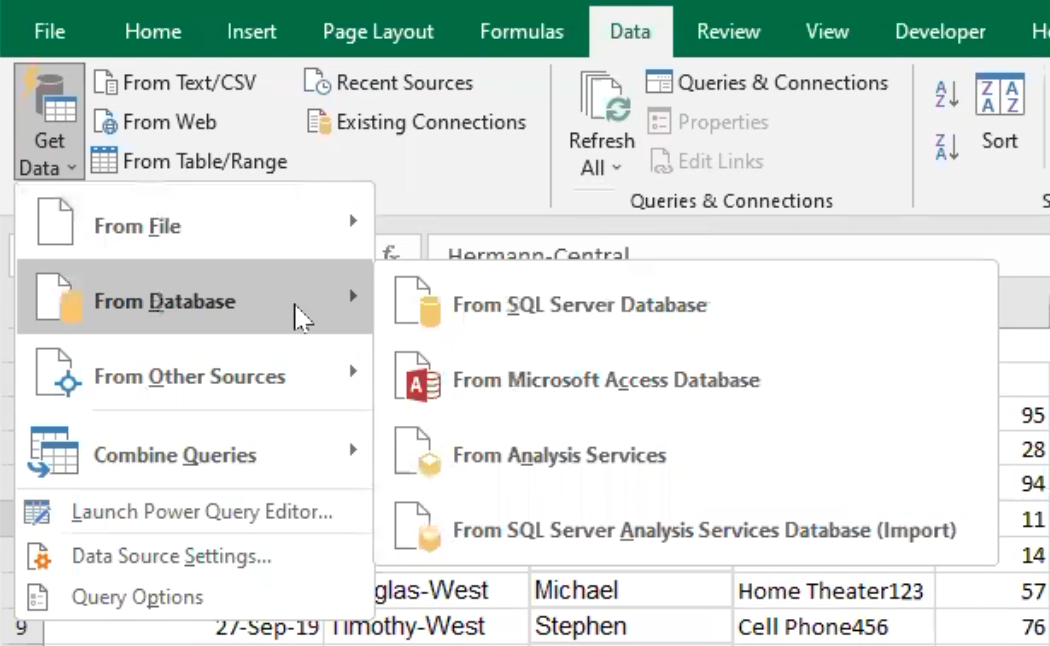
- Other data sources: Power Query also provides connectors for other data sources such as Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), OData feeds, Azure Data Lake Storage, Microsoft query, web or online sources and more.
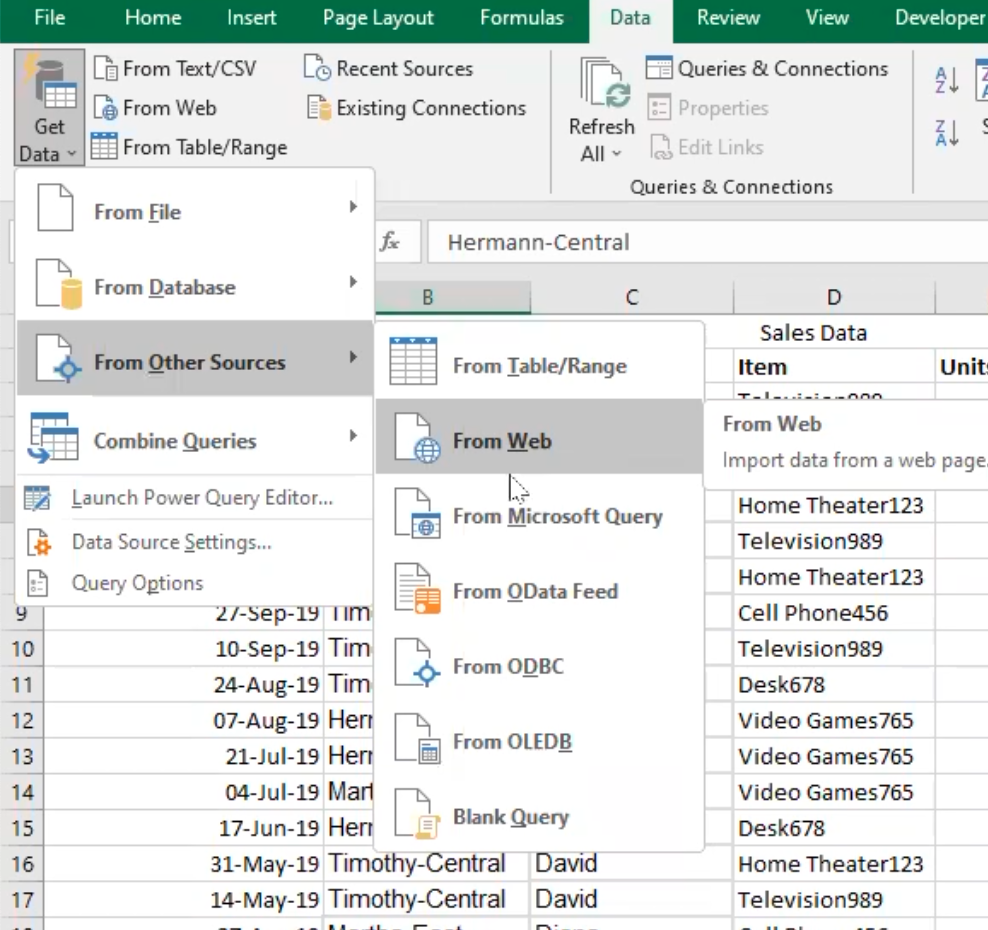
Note: To access these data source options, you can go to the "Get Data" option on the Home tab in the Power Query Editor. From there, you can choose the type of data source you want to connect to and follow the steps to import data into Power Query.
Load data from folder in power query
To load data from a folder in Power Query, follow these steps:
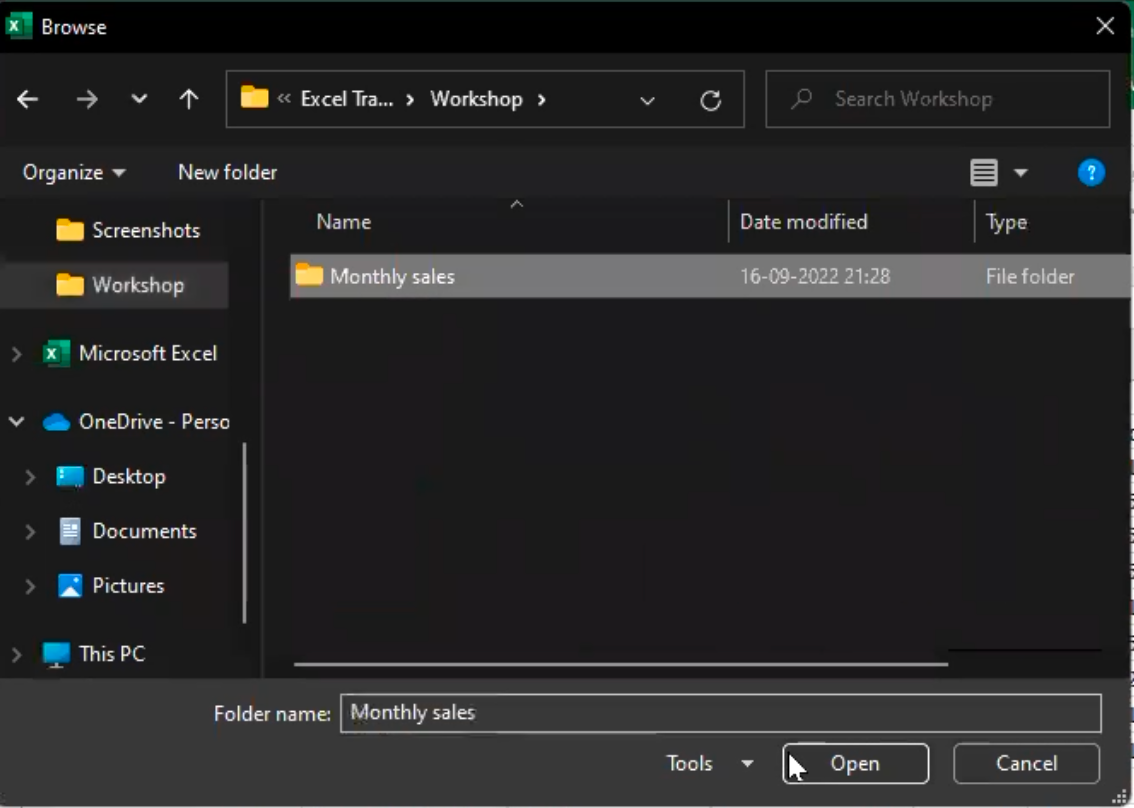
- Open Power Query by clicking on the "Data" tab in Excel and selecting "Get Data" > "From File" > "From Folder".
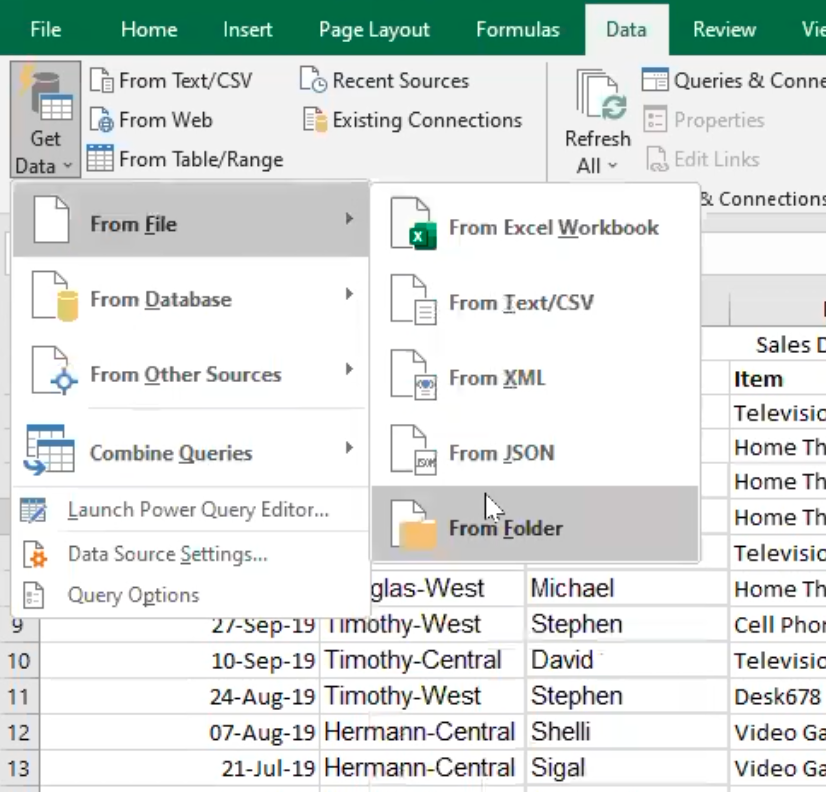
- In the "From Folder" dialog box, select the folder where your data is stored and open
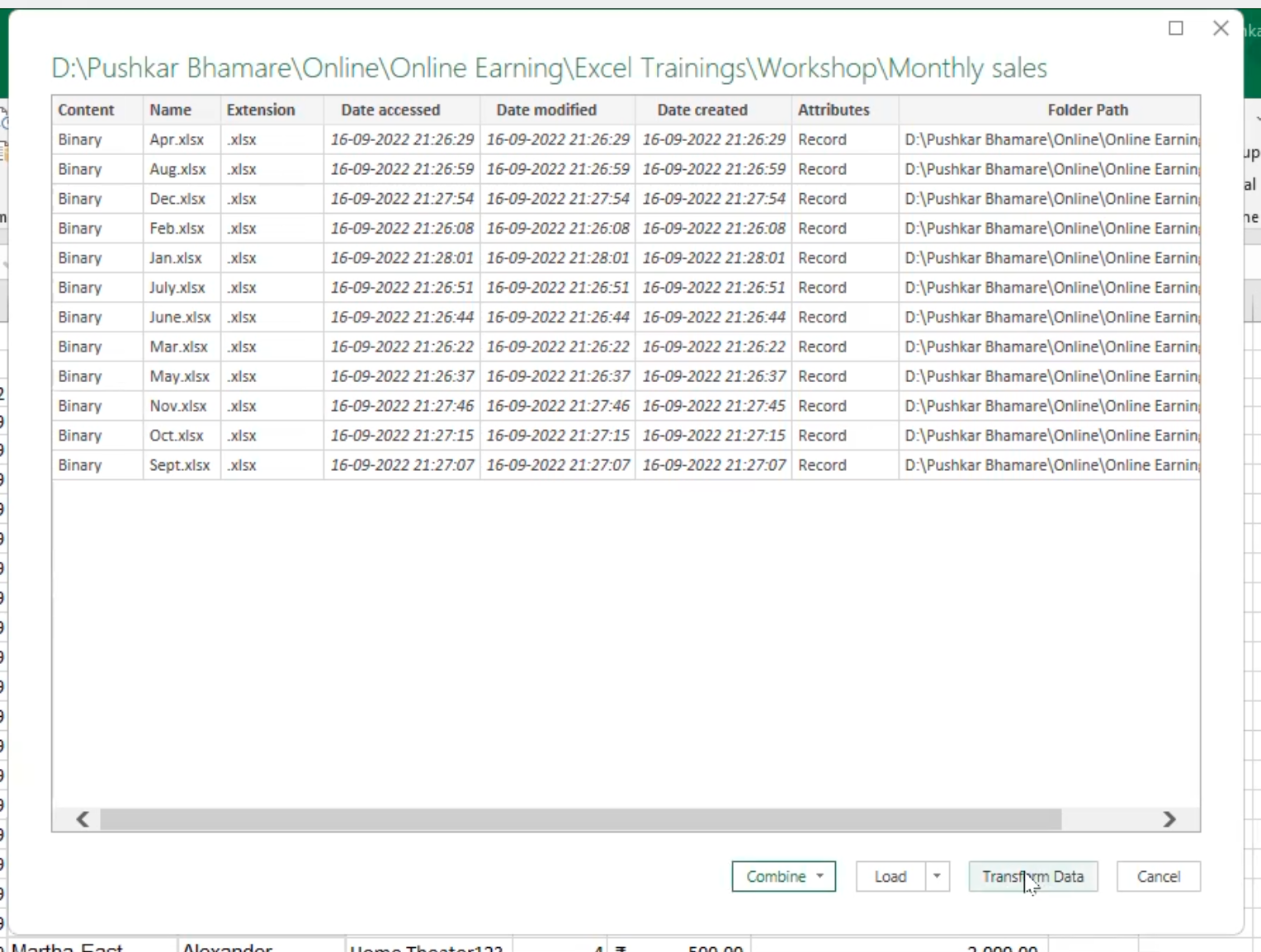
- This launches the power query navigator with the different options. Select the “transform data” since I will still be performing some transformation operation on the data.
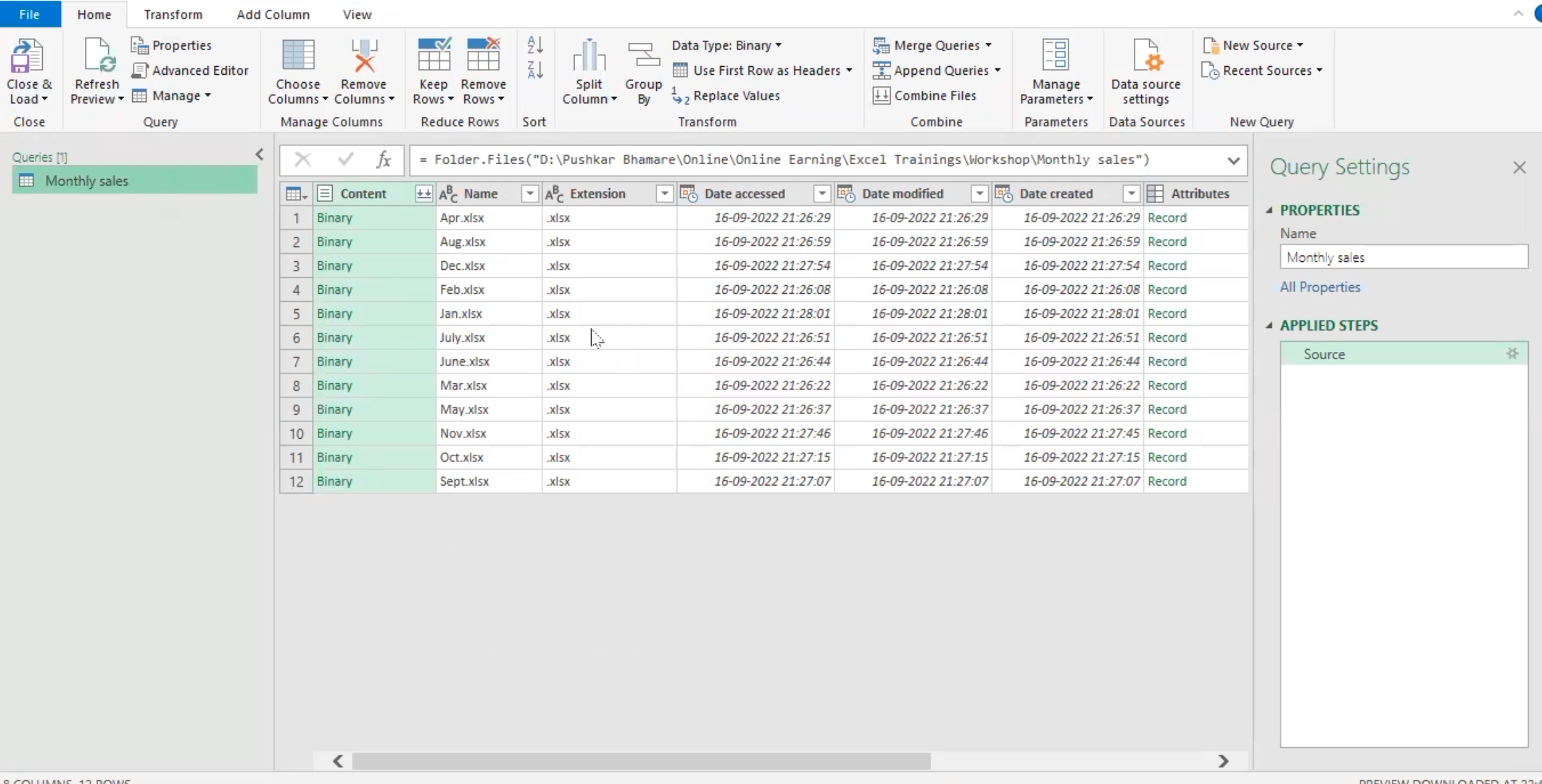
- This will automatically launch the power query editor.
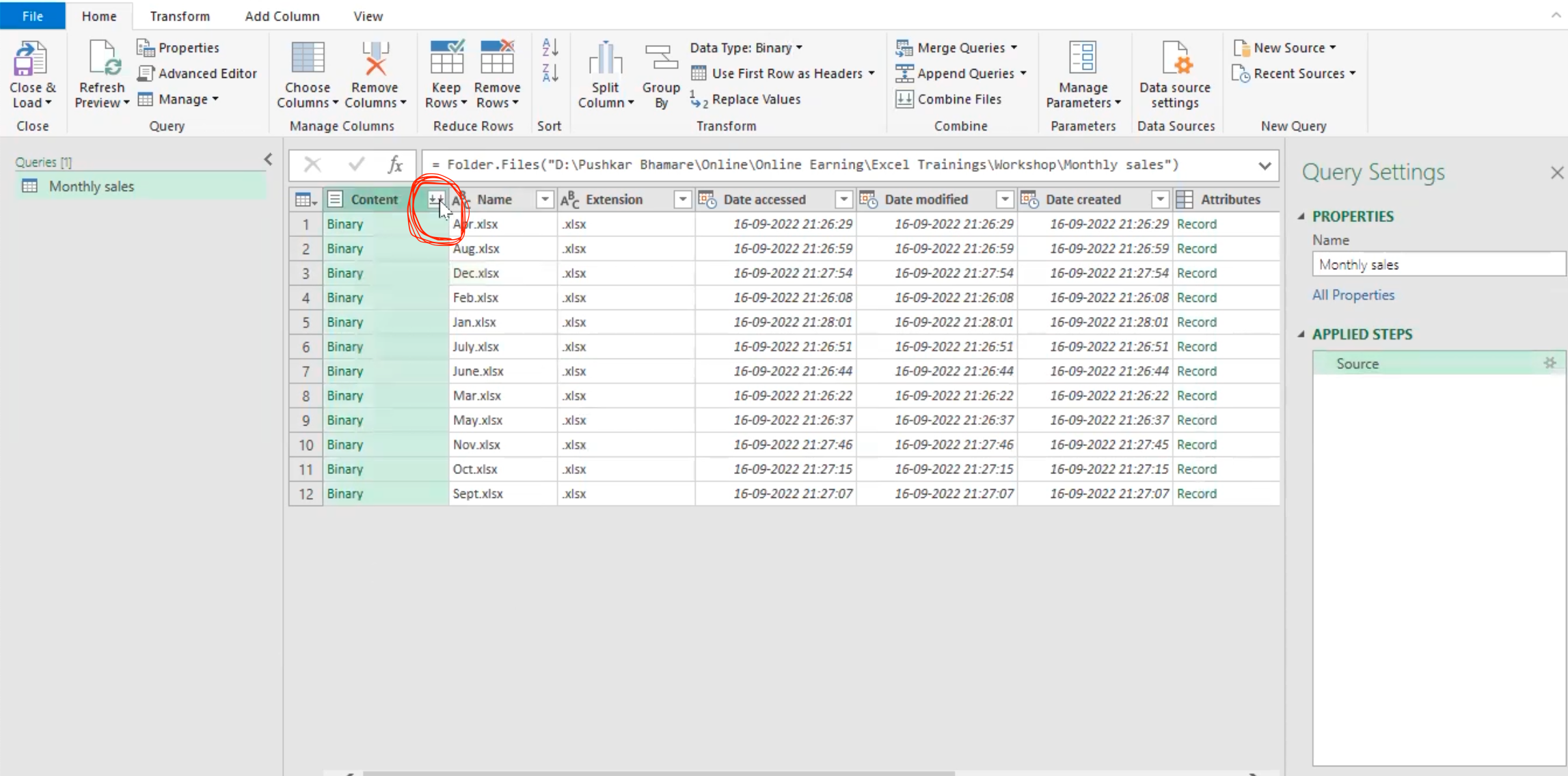
- Then, click on the circled arrow in the content column to combine all the data in the folder.
- This launches the navigator for selection of sample file and table to which the data should be combined. After the selection, click “Ok” to combine the data.
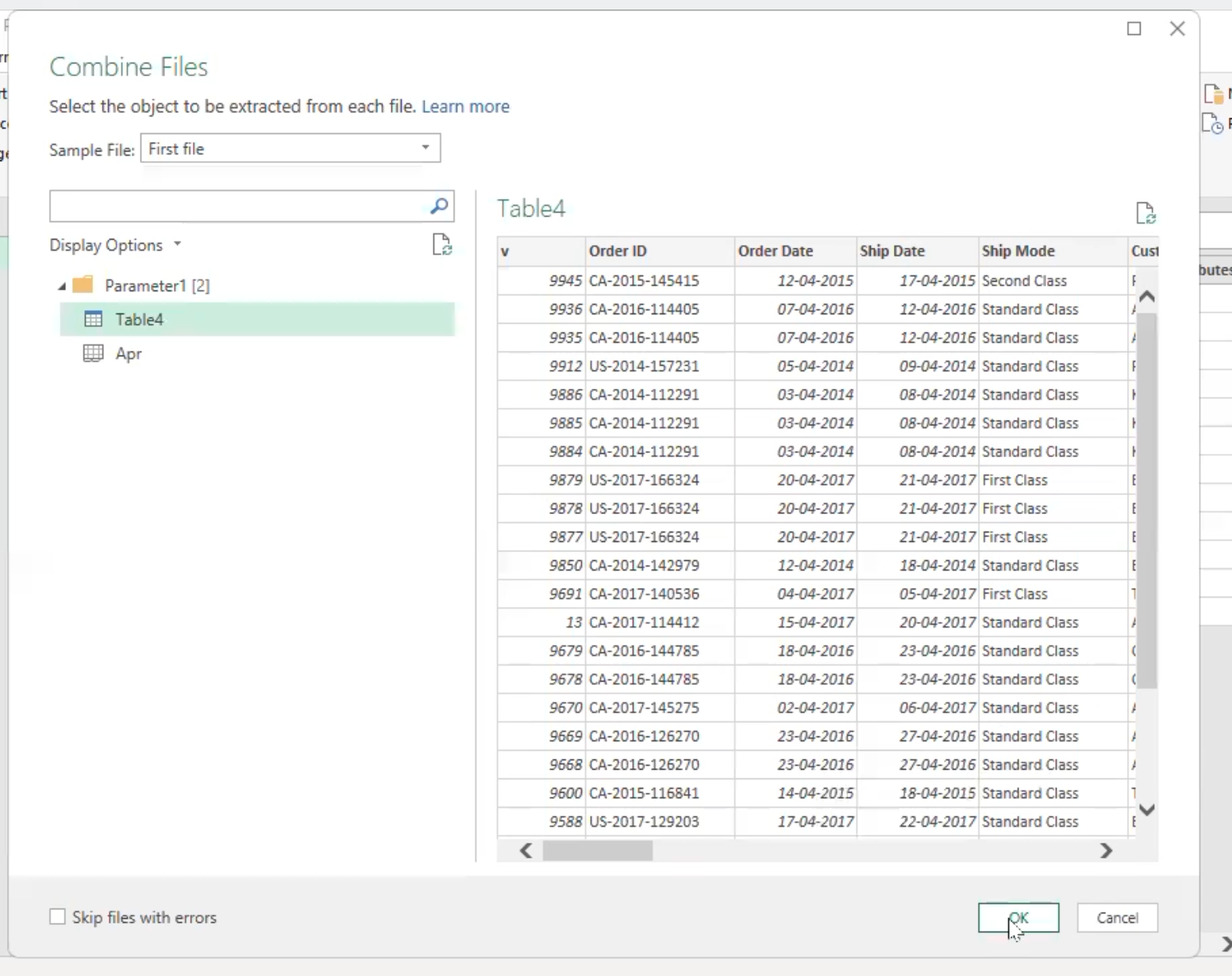
- The data will be combined, and many queries will be created, which includes the “sample file”, “transform file” and “transform sample file” and the file is fully combined.
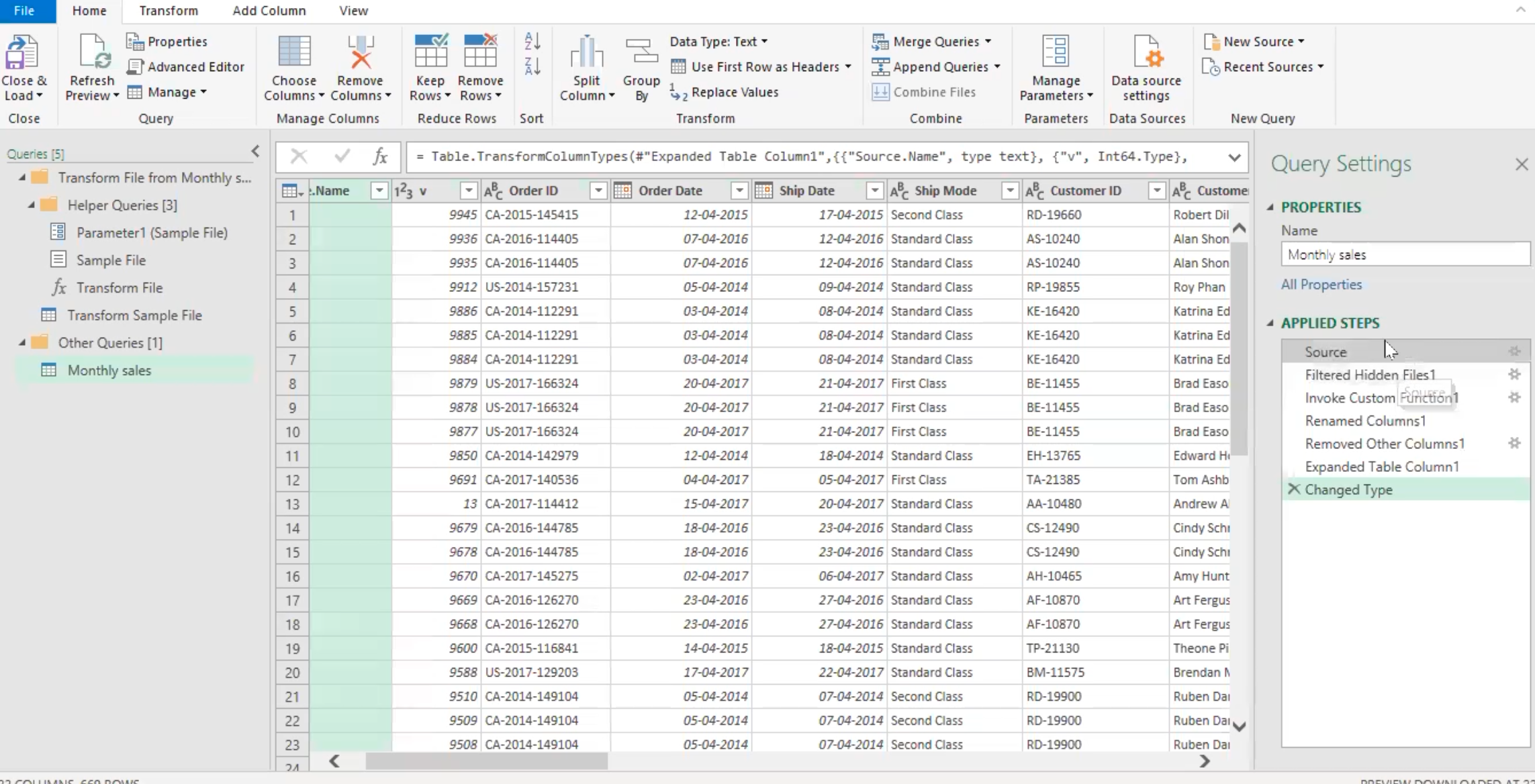
Close and load option and data types
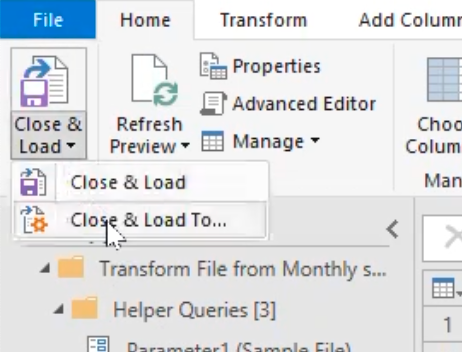
- There are two major options here, the first is to close and load into excel, but I will be selecting the “close and load to” option.
- The second option is to “close and load to” some kind of “table” or “pivot table report” or “pivot chart” or “only create connection”.
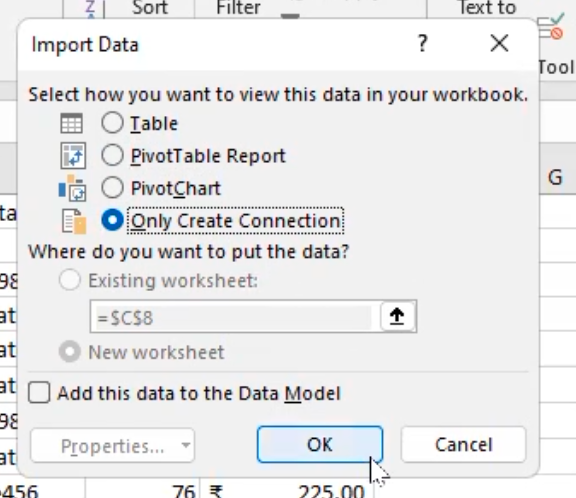
- Then, I will be selecting “only create connection” - as it will not load the file into excel but create “only connection” with all the files in the folder.
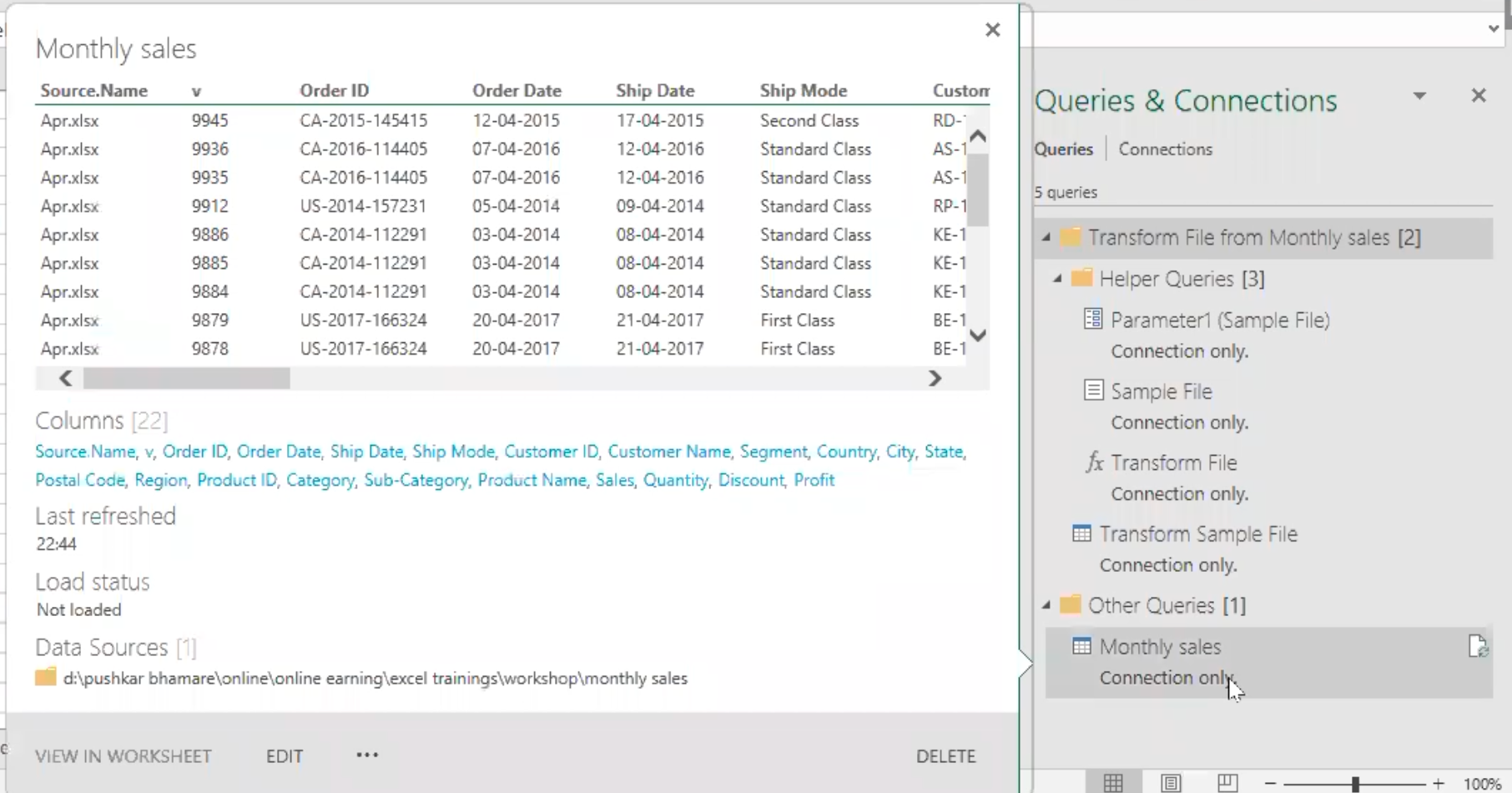
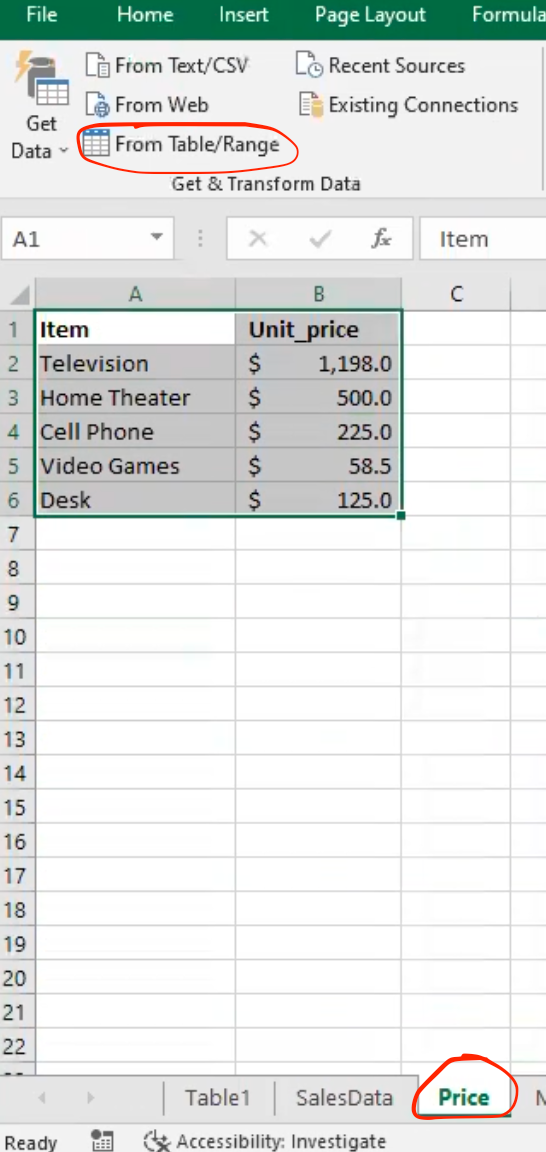
- Since there is another sales data in the excel sheet “table 1”, I will load it into Power Query also. To do that, select the table range.
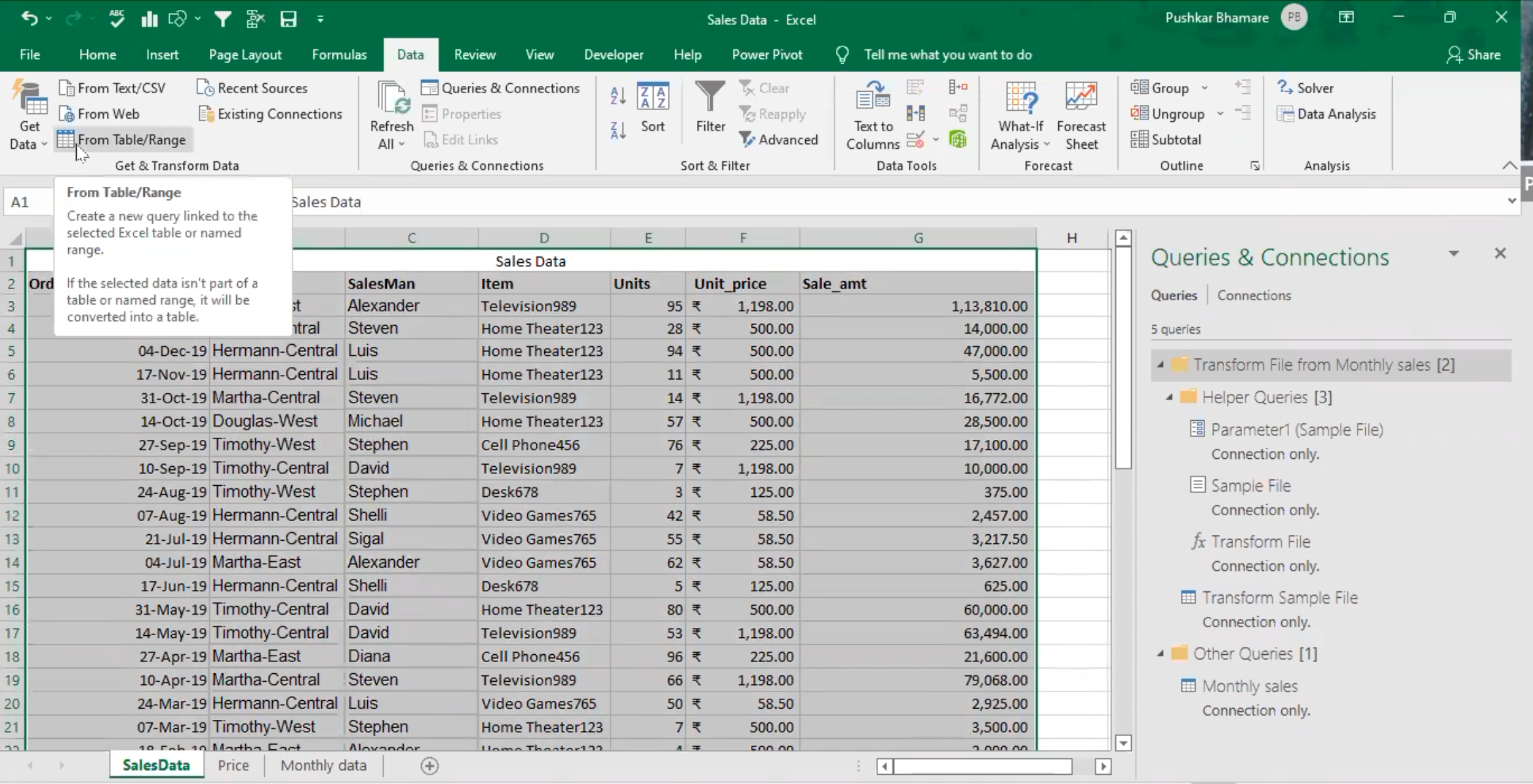
- This loads the data “table 1” into power query editor.
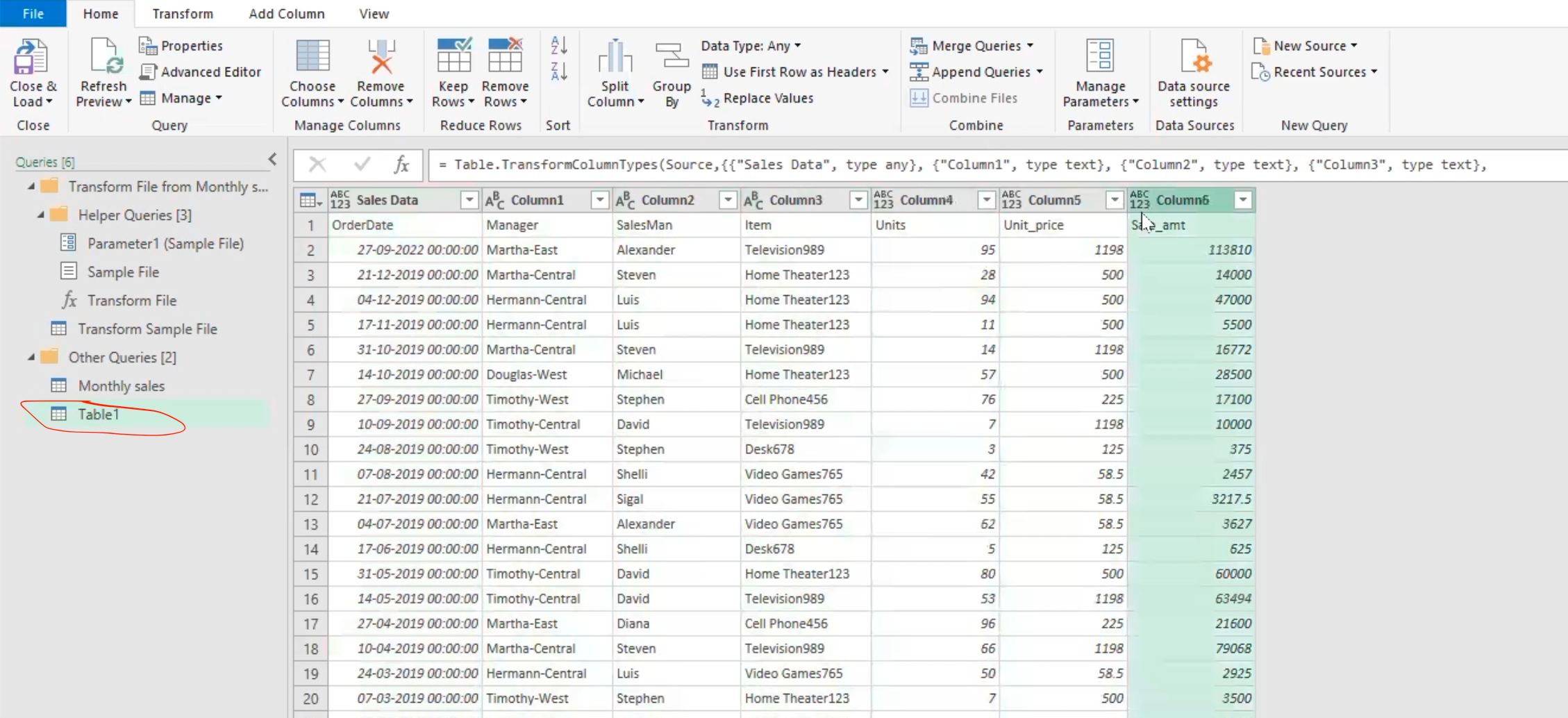
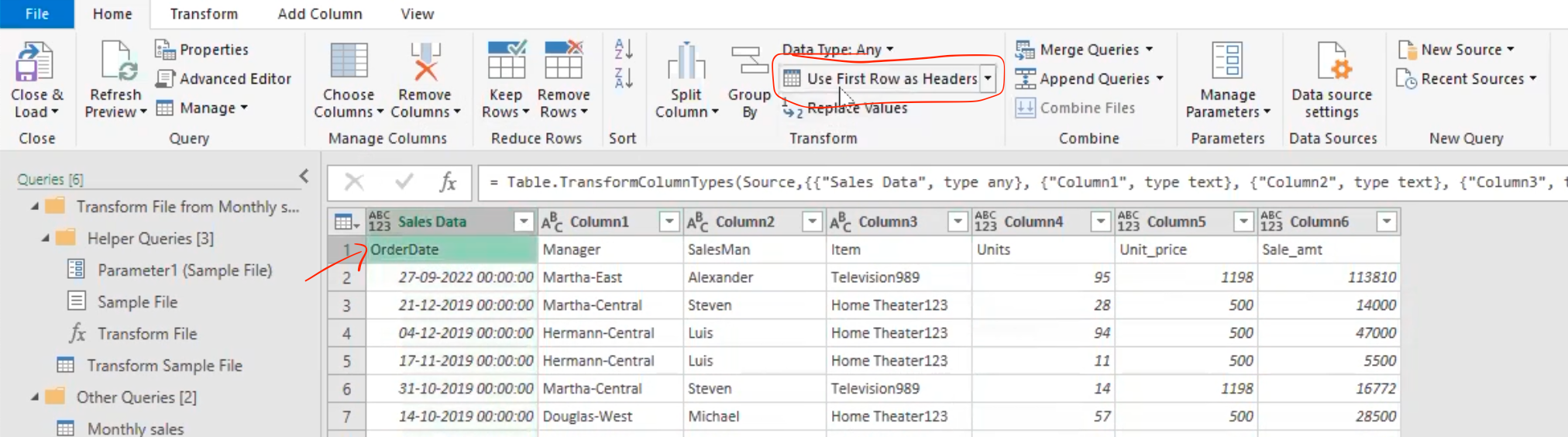
- Select usefirst row as header for proper data column representation.
Split and extract operation in power query
- Split the item column as it contains the name of the item and the digit. Click on split column in the home tab and split by Non-Digit to Digit
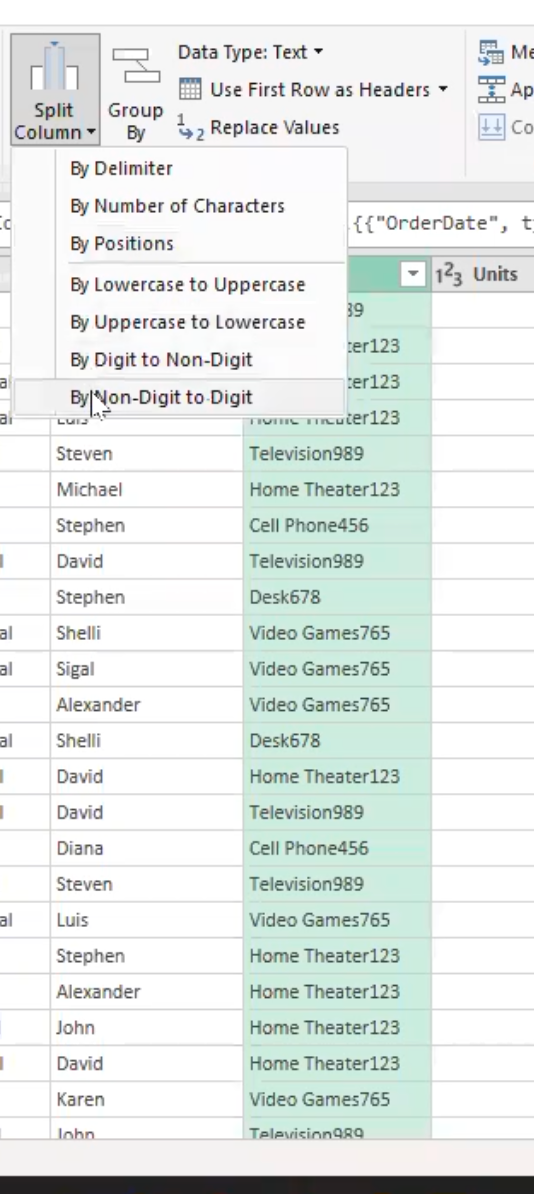
- This automatically creates a new column and move the digits at the end to that column, which I will rename as “Item number”
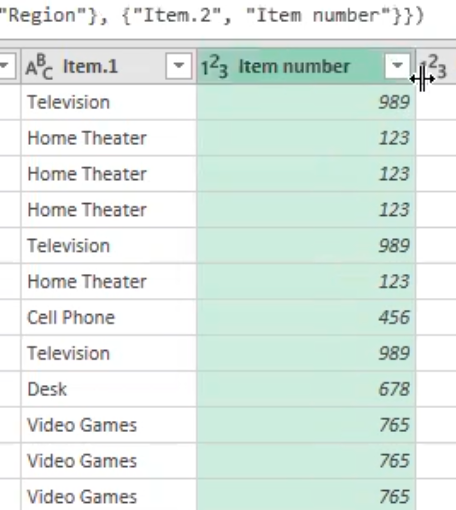
- Also, for the manager column, split the names of the manager from their respective region. Select split column by delimiter and power query automatically identifies the hyphen (-)
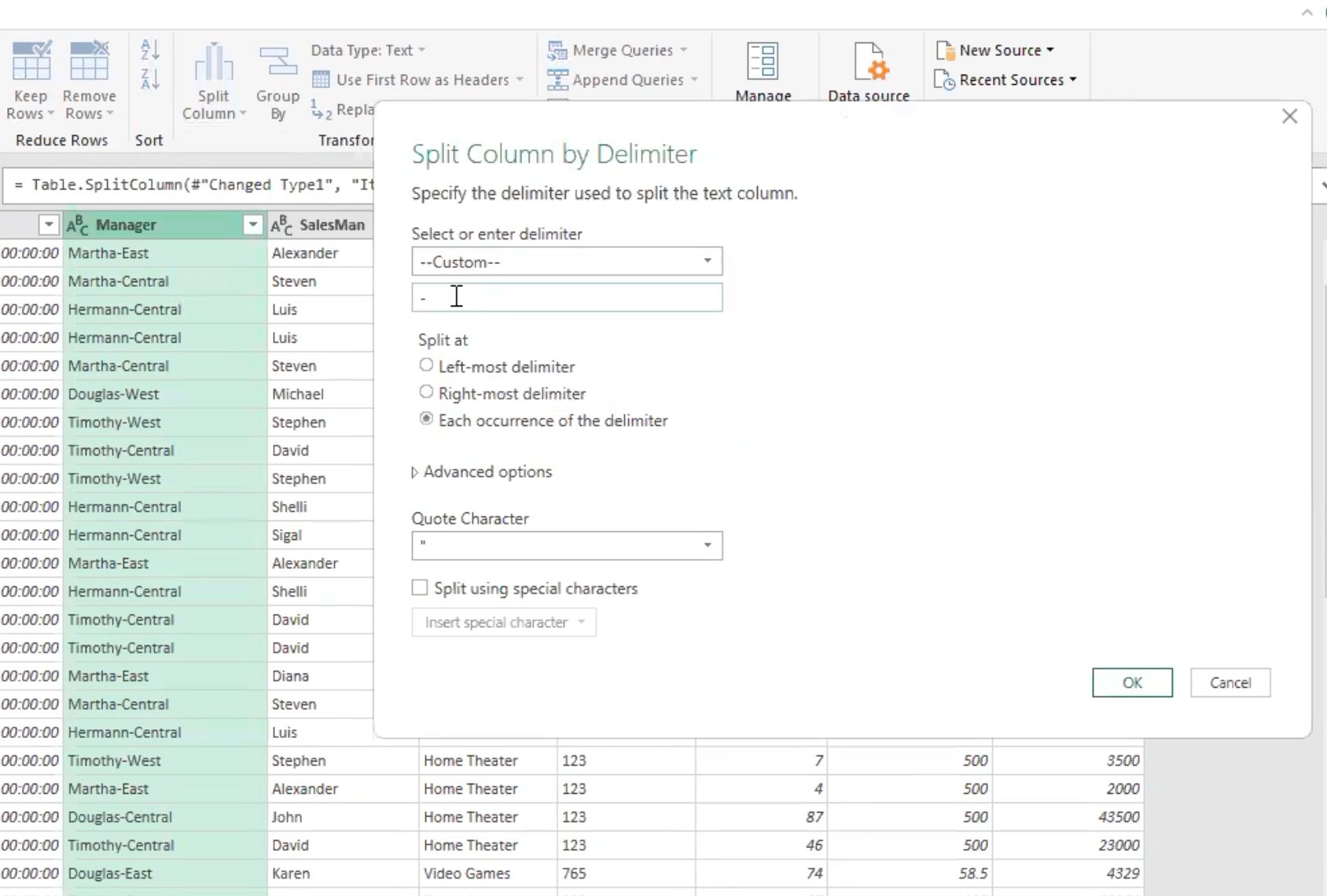
- This automatically creates a new column which I will rename as “region”
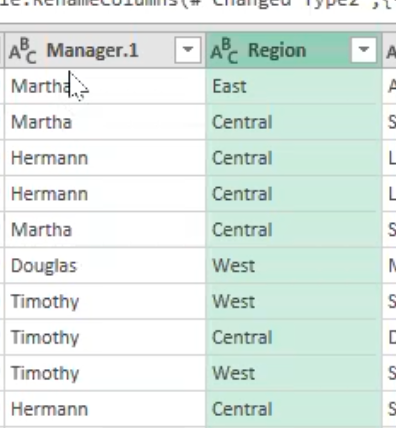
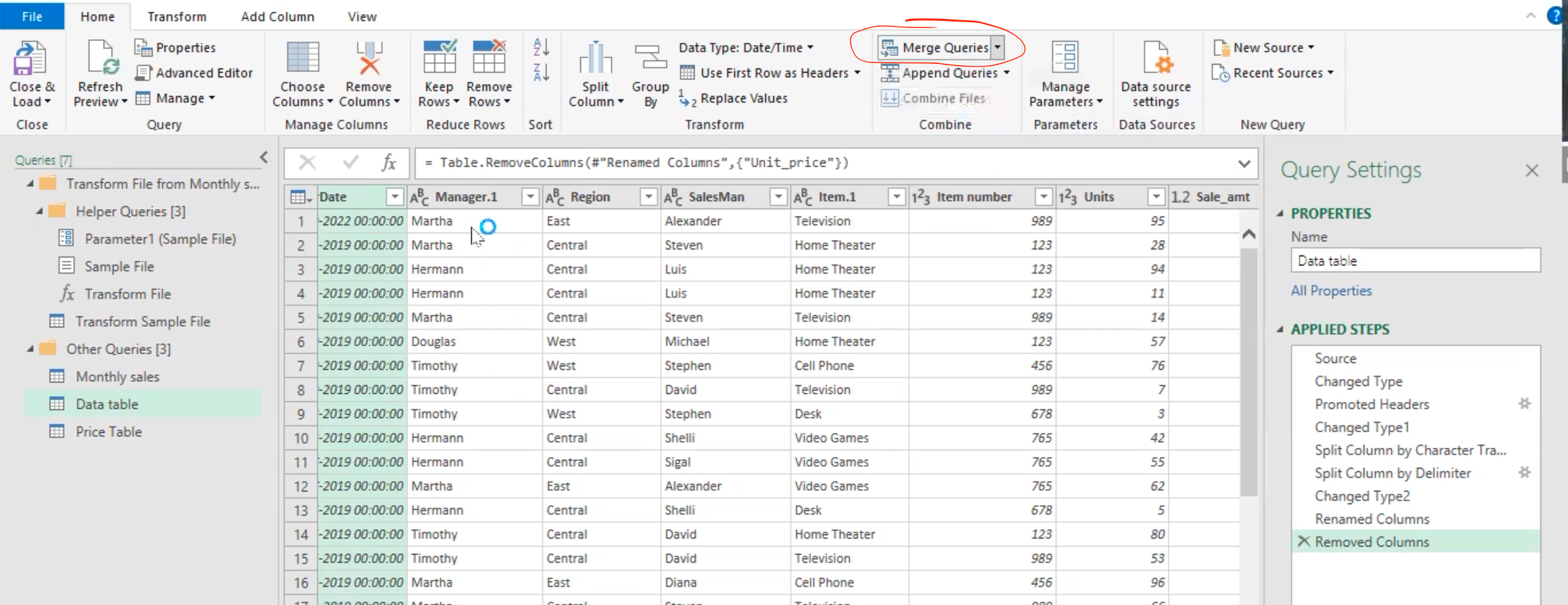
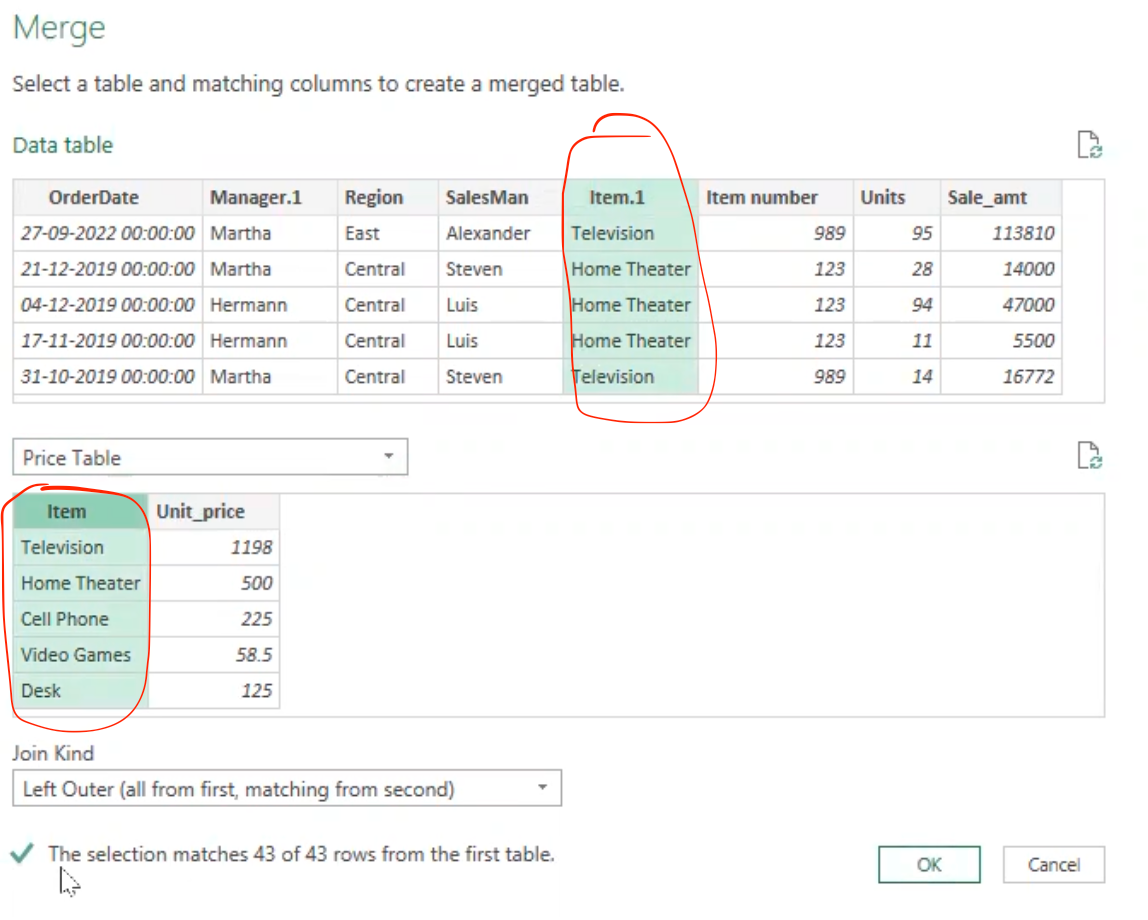
Merge queries in power query
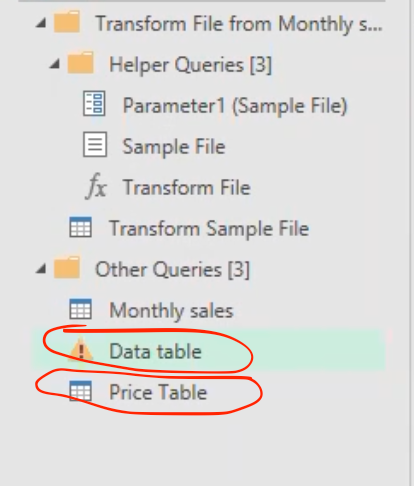
Note: Rename the combined table in power query to be “data table” and load the “price table” from excel into the power query editor in a bid to get the unit price for each items using the merge query option.
- After getting the data into power query, then select “merge queries”
- It pops up the merge navigator, which has automatically selected the Data table and then I will select the price table
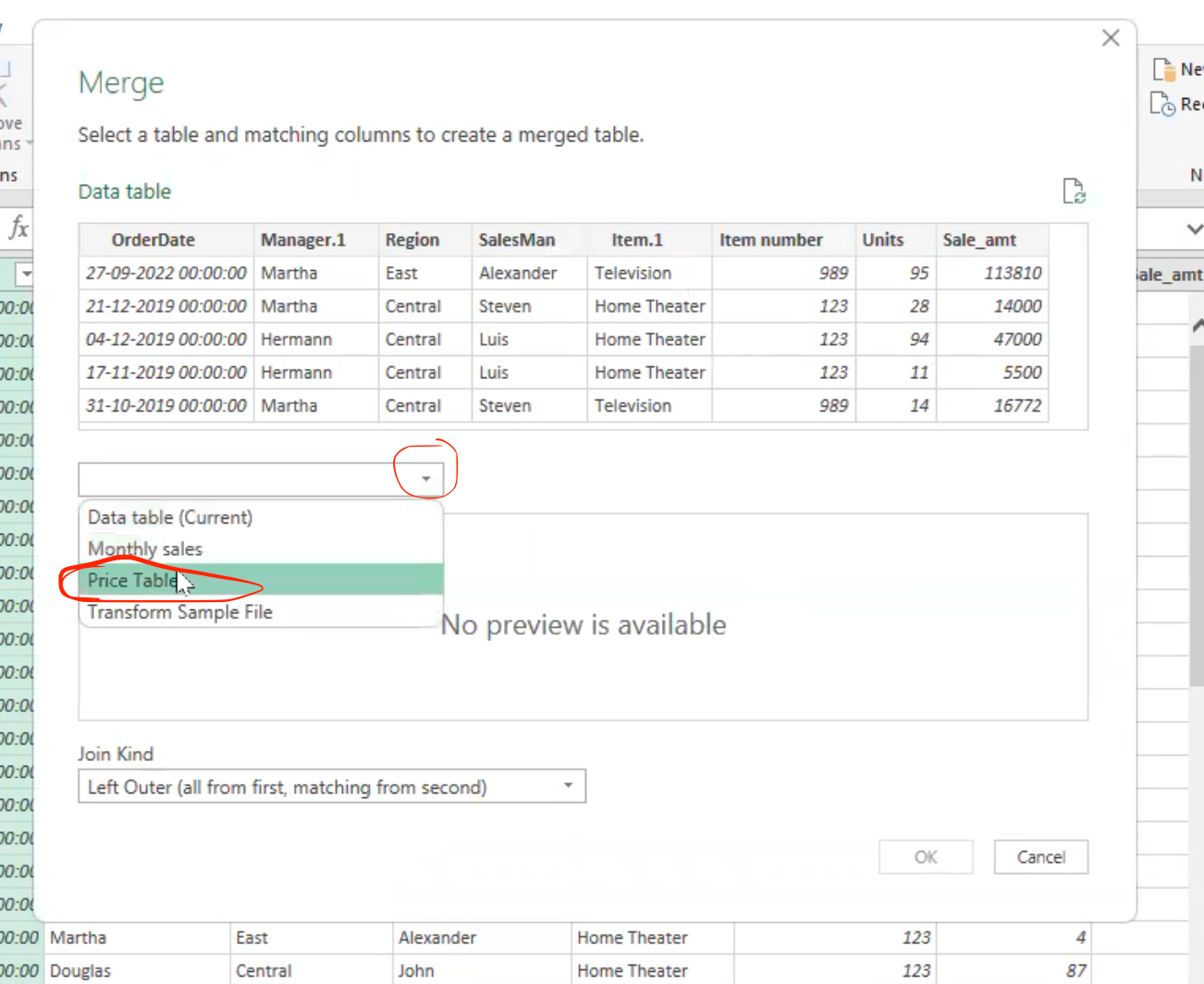
- Select the similar column you want to merge on - which is the item column in both table, then select “Ok”.
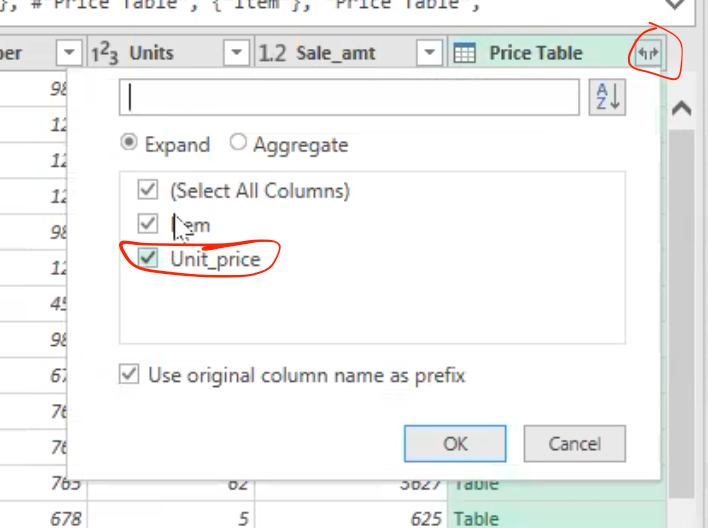
- This merges the table and there is need to unwrap the column that is required to be visible on the table, which is the” unit price column.”
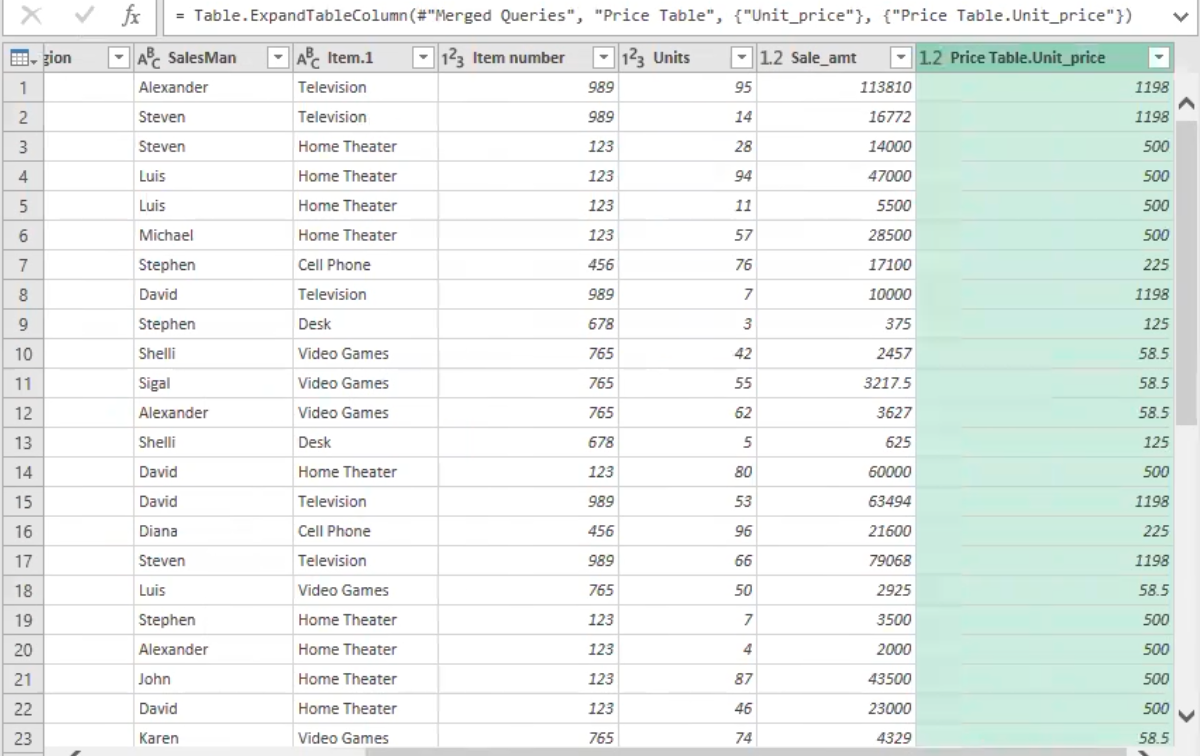
- This automatically unwraps the unit price column and merge with the unique item in the data table
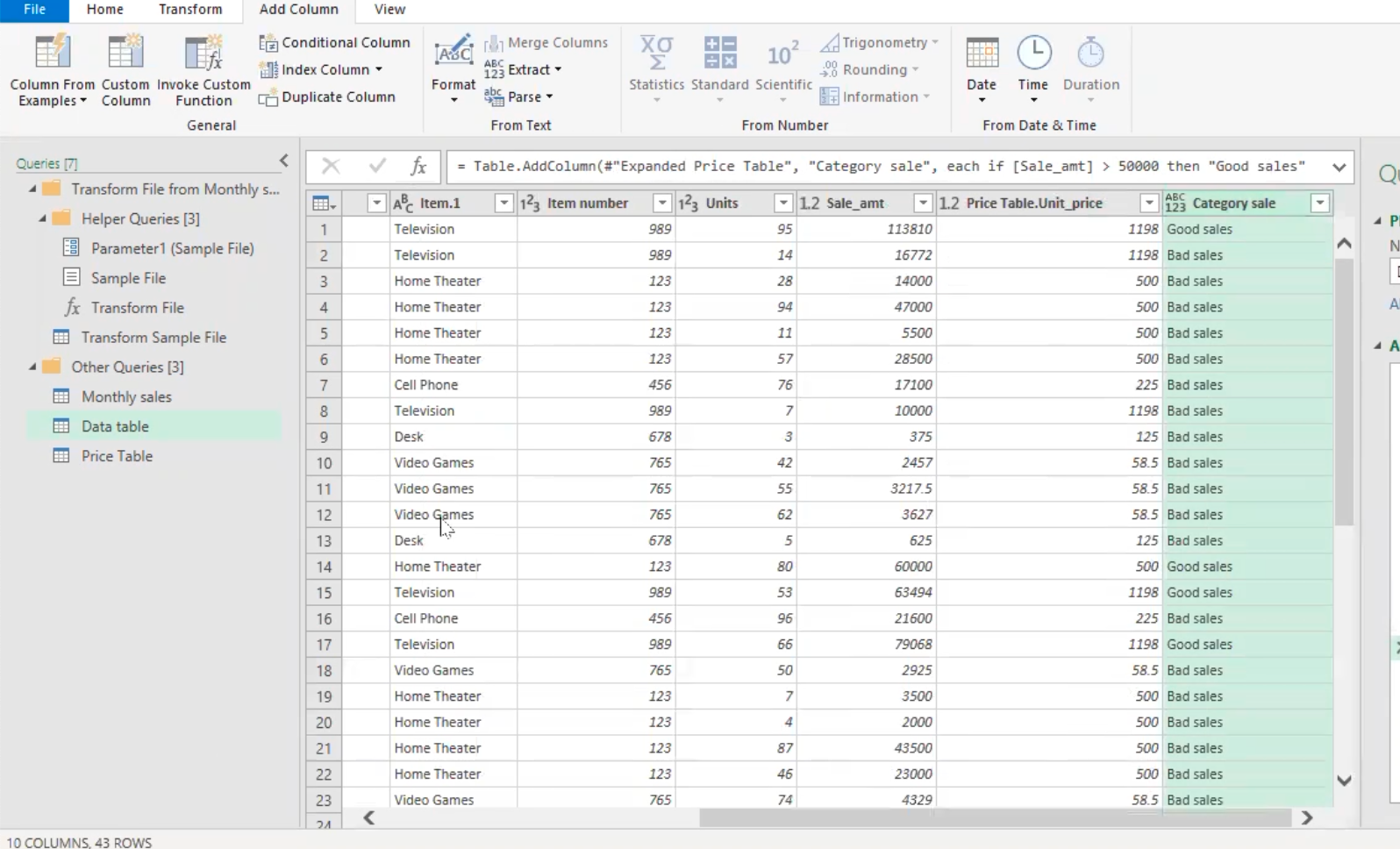
Conditional column in Power Query
This is basically creating a new column by using conditional statement to fill the column relative to an existing column.
- Select the “add column” tab, then click on “conditional columns”. This pops out the add conditional column navigator, where you can then use your if statement.
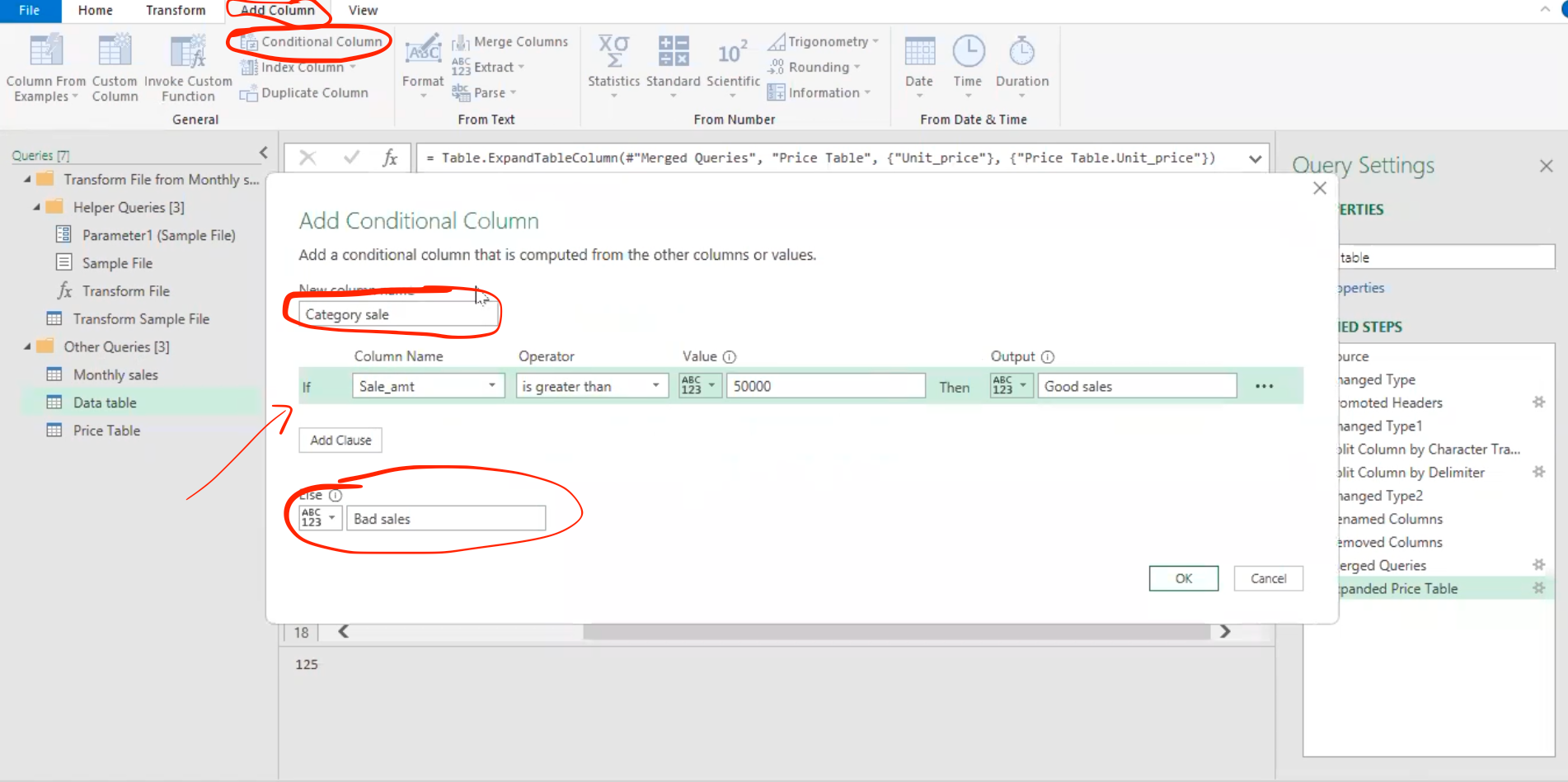
Note: The above “if statement” is categorizing sales with sales amount greater than 50,000 to be a “good sales” and otherwise “bad sales”
It is important to note that you can also manipulate data types with this feature in a bid to make your data more friendly for analysis. This includes converting or breaking down date features to time, quarter, year, or even weeks.
- This automatically creates the “Category sales” column
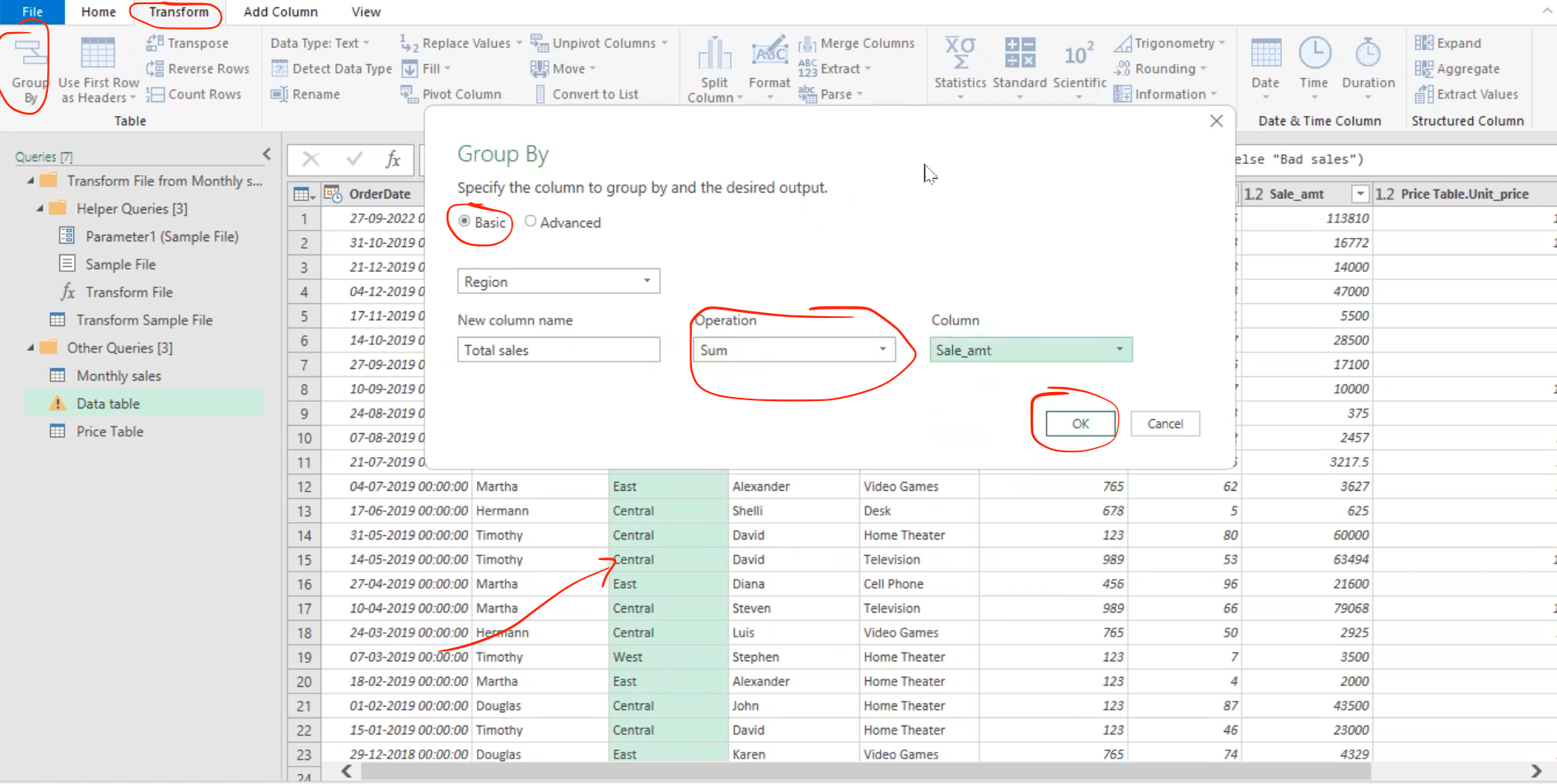
Group by function in Power Query
This is basically like a summary function in power query, it is similar to what happen when a pivot table is created in excel. This feature has the “basic” which is used for grouping by a single column and “advanced” which is used for grouping by multiple columns
- Let’s say we want to understand, how much sales do we have from each region in our sales data.
Select the column you want to group by and go to the Transform tab, then click “group by”, which will the pop out the Group by navigator. I will select basic and fill in the operation to be performed with respect to the column to perform it.
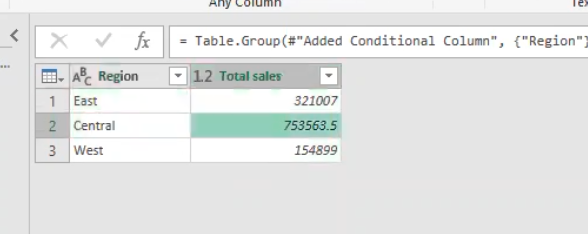
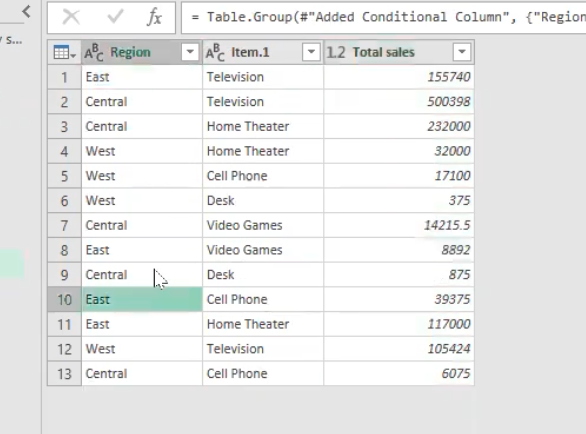
- This gives this result of each region and the total sales from them respectively as shown in the table below.
- I will also be grouping by multiple columns (Region by Item) using the advanced function to calculate the sales amount also.
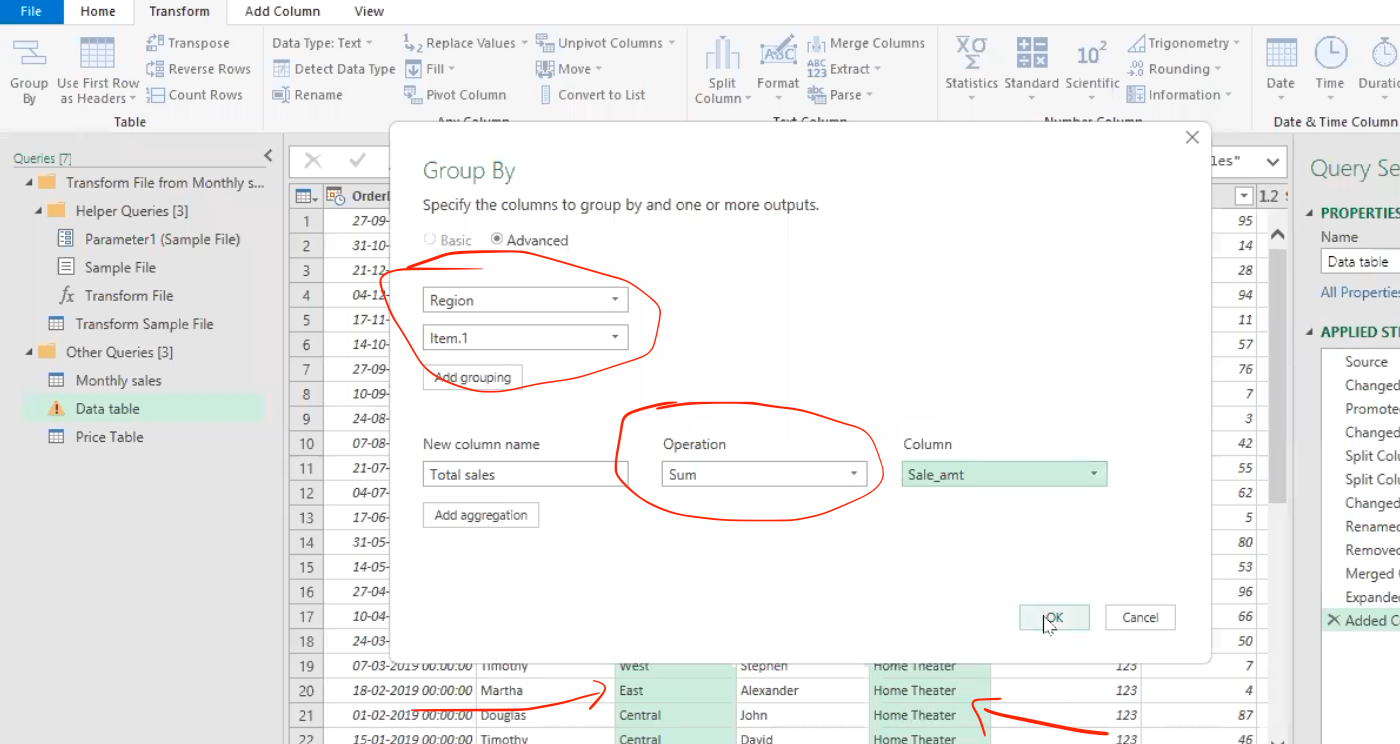
- This gives this result of each region by respective item and the total sales from them respectively as shown in the table below.
Unpivot and pivot columns in Power Query
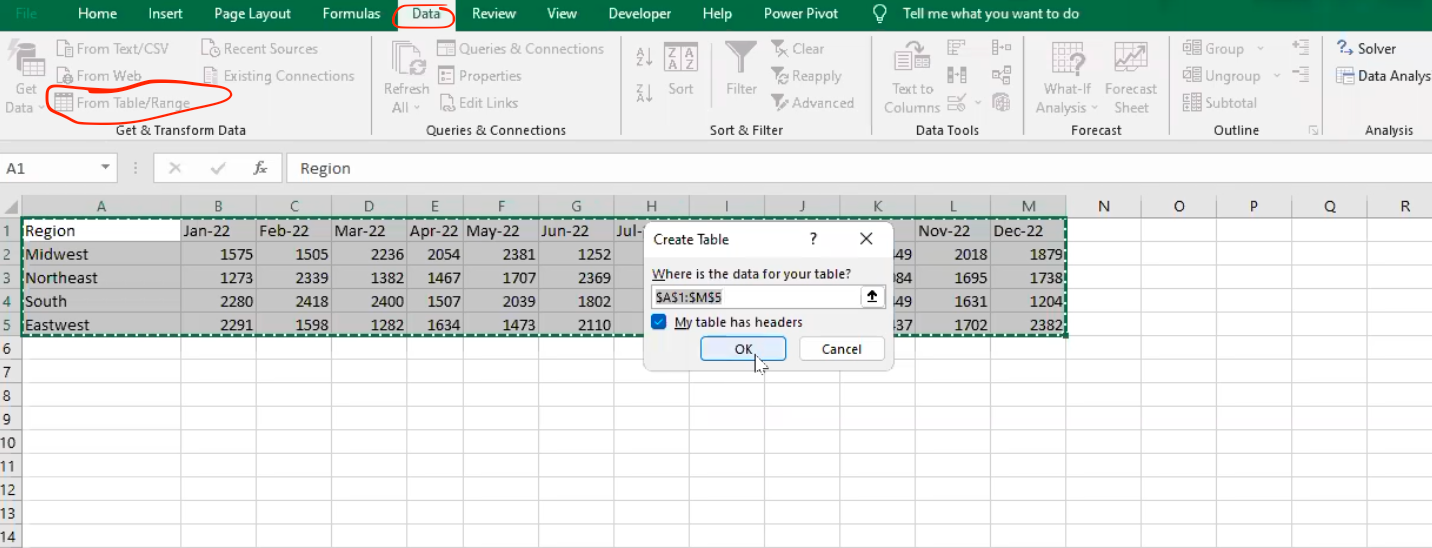
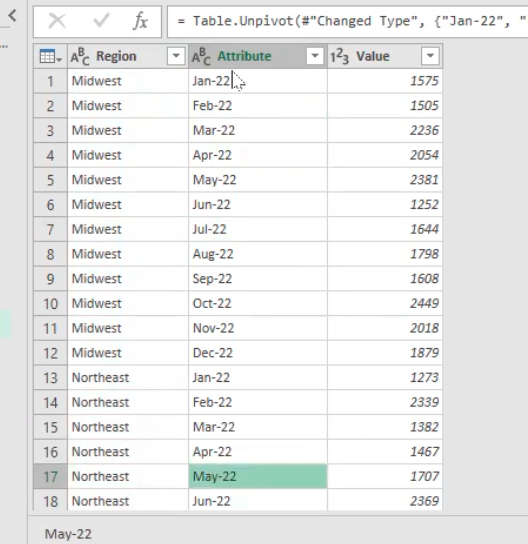
This is a data for sales by month with respect to regions as shown below, the data will then be moved into power query for further analysis.
- Select the “data tab” in excel and “from table/range” to move to power query.
- Rename the table as “sales by month” in power query.
- Then, select all the months that is to unpivot for better view during analysis
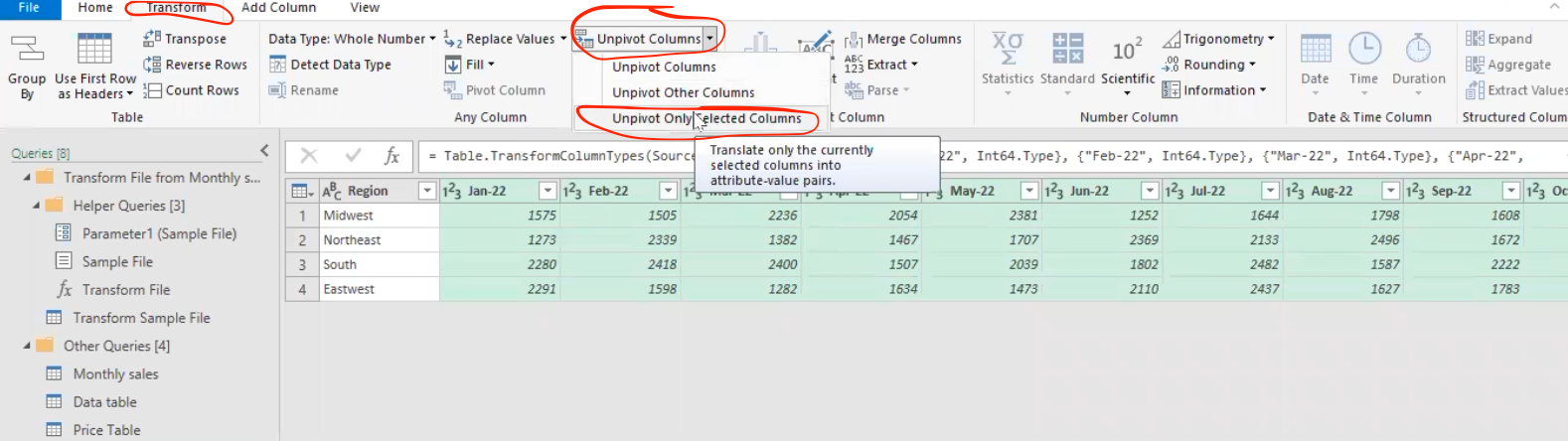
- This will then be converted into a column data which gives the region, months and sales amount.
Note: You can further apply the group by function to analyse the data to get the sales by month or sales by region or even advanced group using multiple columns
It is also important to understand that unpivoting columns transforms data from row to columns, while pivoting column transform data from column to rows
Append queries in Power Query
In Power Query, "append queries" refers to the process of combining data from two or more tables or queries by appending the rows of one table or query to another. The resulting table will have all the columns from both tables and all the rows from both tables.
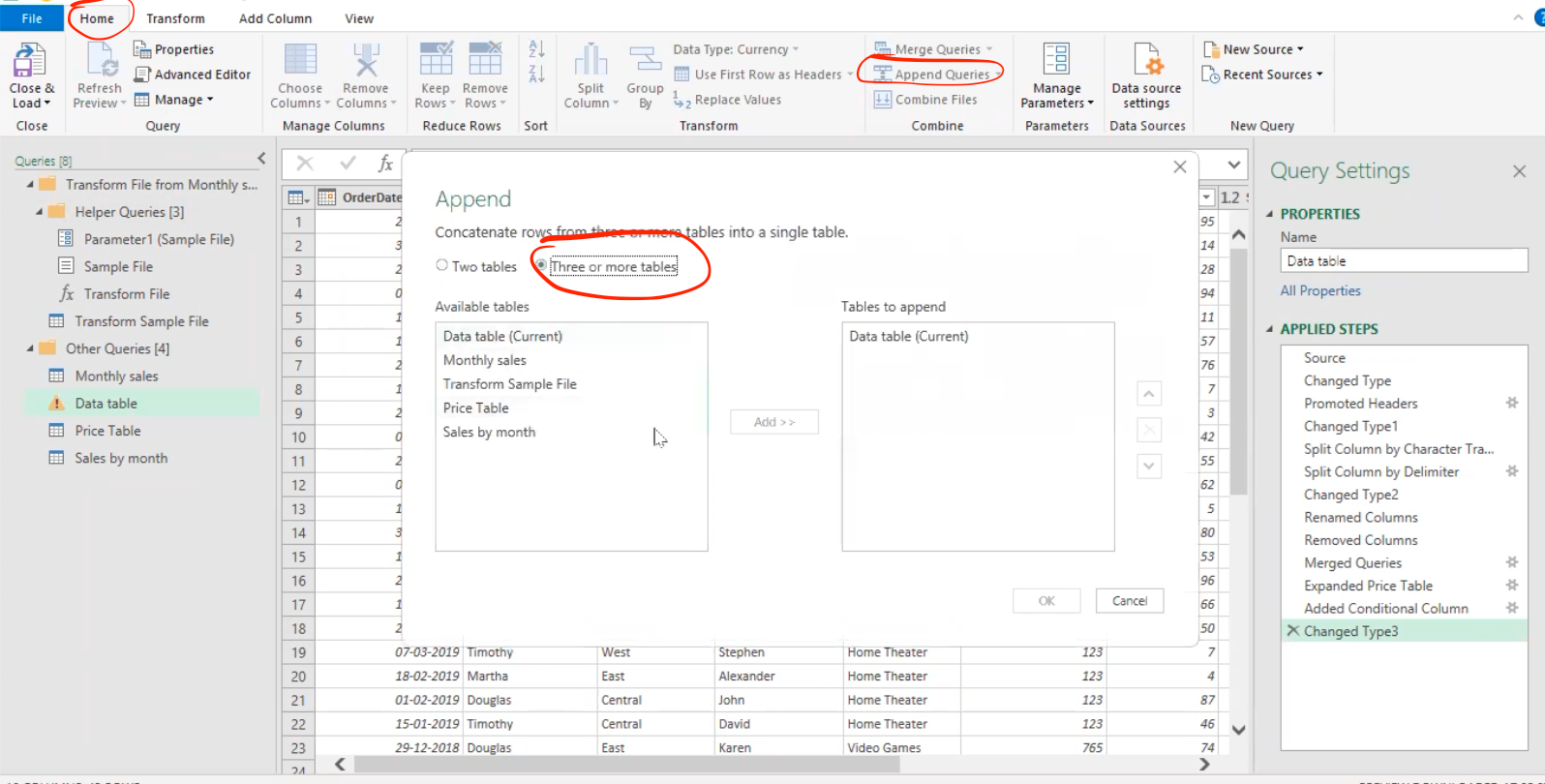
Note: Appending queries can be useful when you have multiple data sources or multiple tables with similar structures that you want to combine into a single table. For example, you might have sales data from multiple regions or multiple months that you want to combine into a single table for analysis.
Conclusion
Power Query is a powerful data transformation tool that is available in Microsoft Excel, Power BI, and other Microsoft applications. It provides several built-in tools and functions that you can use to transform and automate reporting of multiple datasets. Transformation in Power Query is the process of cleaning, shaping, and manipulating data to prepare it for analysis. It is also a crucial step in data preparation because it ensures that data is in a consistent format and free of errors, missing values, or duplicates. Hence, the need of understanding this tool cannot be undermined or overstated for data analyst or analytics engineers.
If you want to explore more on building your Microsoft Excel skill, visit our learning path HERE
Also, if you want to get started with data analytics and looking to improving your skills, you can check out our Learning Track
Empowering individuals and businesses with the tools to harness data, drive innovation, and achieve excellence in a digital world.
2026Resagratia (a brand of Resa Data Solutions Ltd). All Rights Reserved.
